Package for the estimation of early stage battery degradation mechanism and lifecycle monitoring
Project description
ARCANA

ARCANA: A ttention-based R e C urrent C ognitive A lgorithm for N eural A nalysis
(Logo conceptualized and designed by Midjourney <https://www.midjourney.com/>)
Introduction
ARCANA is a Python package that implements, an LSTM-based Seq-to-Seq architecture with an integrated attention mechanism, designed for the early-stage analysis and lifecycle monitoring of battery degradation.
Features
The model provides robust multi-task prediction capabilities through its modular design and the ability to dynamically adjust. It processes a wide range of historical battery cycle data to provide foundational insights for initial degradation detection. Incorporating predefined operational parameters, such as discharge rates and cycle numbers, ARCANA offers a dual analytical approach. This approach, coupled with the model’s inherent ability to include uncertainty in its predictions, presents ARCANA as an essential framework, which enhances the strategic development of battery maintenance protocols as well as reliability and longevity in energy storage applications.
Documentation
The documentation for ARCANA is available at ARCANADocs.
Installation
For installation instructions, please refer to the [Installation Guide](docs/installation.rst) within the documentation directory. A quick start can be achieved by downloading the pip packages by running this command in your terminal:
$ pip install arcana-battQuick Start
To begin using ARCANA for battery degradation analysis, configure the procedure parameters in the configuration files. The following possibilities are available:
Training: If naive training is enabled in the configuration, ARCANA will start the training process using the provided dataset and model parameters.
Hyperparameter Tuning: If Optuna tuning is enabled, ARCANA will optimize the model’s hyperparameters using the
TuneProcedurefor the specified number of trials.Transfer Learning: If transfer learning is enabled, ARCANA will proceed with the fine-tuning of the pre-trained model using the strategy specified (e.g.,
decoder).Prediction: Finally, if the predicting flag is set, ARCANA will perform predictions on the pre-trained model for the provided data.
Here is a sample code snippet to get you started:
from arcana.logger import logger
from arcana.procedures import training, tuning, predicting
from arcana.procedures import finetuning
logger.setup_applevel_logger(file_name="arcana_debug.log")
log = logger.get_logger("arcana.main")
def run_test():
arcana_procedure = training.TrainProcedure()
if arcana_procedure.procedure_config.naive_training:
arcana_procedure.training()
if arcana_procedure.procedure_config.transfer_learning:
arcana_procedure = finetuning.FineTuning(tl_strategy="decoder")
if not arcana_procedure.procedure_config.optuna_tuning:
arcana_procedure.training()
if arcana_procedure.procedure_config.optuna_tuning:
tuning.TuneProcedure(procedure=arcana_procedure).tuning()
if arcana_procedure.procedure_config.predicting:
predicting.PredictProcedure(arcana_procedure).predicting()
if __name__ == "__main__":
run_test()Ensure that you have installed all required dependencies and have the necessary data prepared as per ARCANA’s input format.
Configuration
ARCANA is designed to be flexible and adaptable to a wide range of scenarios in battery health prediction. To tailor the predictive modeling to your specific dataset and analytical needs, ARCANA utilizes two main configuration files: general_parameter.ini and model_parameter.ini; adjust these configurations to match the characteristics of your battery data and the specificities of the analysis you intend to perform with ARCANA.
General Configuration
The general_parameter.ini file serves as the central hub for setting up the main aspects of ARCANA. This configuration file is important for defining the workflow and data management for the predictive analysis. The following are the key sections and their respective parameters:
General Settings: This section captures the settings for the general workflow, including unique identifiers and paths to essential data and/or model files. It allows you to specify the location of input data, the name of the dataset, and paths to pre-trained models and scalers.
Data Specifications: Here, you can define the structure and specifics of your input data. Parameters include the headers of your dataset, the number of samples to consider, and the maximum number of cycles to use. Additionally, you can set the ratios for splitting your data into training, validation, and test sets.
Procedure Flags: This section allows you to toggle various procedural steps in ARCANA’s workflow. You can enable or disable naive training, prediction, data preprocessing, and hyperparameter tuning with Optuna.
Model Behavior: Adjust the learning rate type and attention mechanism type to suit your model’s learning strategy and the nature of your data.
Optimization and Tuning: Control the extent of hyperparameter optimization by setting the number of trials for Optuna.
Model Configuration
The model_parameter.ini file defines the architecture and behavior of the LSTM-based predictive model. Below is an outline of the key parameters you can configure:
Model Settings: Define the input and output dimensions of your model, the loss function to be used, and the path to any tuning configurations. This section sets the foundational structure of your model.
Loss Functions: Customize the behavior of the loss function used during training. You can specify parameters for different losses, depending on the chosen
loss_type.Optimizer: Set the learning rate and weight decay for the optimizer. These parameters are crucial for the convergence and generalization performance of the model.
Schedulers: Adjust the learning rate scheduling by defining factors for reduction or step sizes for cyclical learning rate adjustments. Proper configuration can lead to better training dynamics and faster convergence.
Model Parameters: Specify the number of epochs for training, the dimensions of the hidden layers, batch size, and other architectural features like bidirectionality and dropout rates. These parameters directly influence the model’s capacity to learn from data.
Encoder/Decoder: Fine-tune the encoder and decoder modules of the Seq-to-Seq model by setting dropout rates and the number of layers. This can help in managing the model’s complexity and its ability to capture temporal dependencies.
Multihead Attention: If your model uses a multihead attention mechanism, configure the number of attention heads for both the encoder and decoder. Attention heads allow the model to focus on different parts of the input sequence for better context understanding.
Early Stopping: Implement early stopping to prevent overfitting. You can define the criteria and patience level, which determines how long the training will continue without improvement in the validation metrics.
Teacher Forcing: Control the teacher forcing strategy during training, which can help in stabilizing and speeding up the training process. Set the start and end ratios, as well as the decay rate to manage how the model transitions from teacher-forced learning to autonomous predictions.
Tuning Configuration
The tuning_parameter.ini file facilitates the hyperparameter optimization process to enhance model performance. It defines a range of values for various model parameters and training settings, allowing for a systematic exploration of the hyperparameter space. This includes configurations for loss functions, learning rates, model architecture specifics, and regularization techniques. The file is structured to allow for both discrete and continuous parameter tuning, in accordance with Optuna, with the ability to specify ranges and categorical choices.
Architecture
Here is a diagram of the ARCANA architecture as a simplified UML class diagram. The classes contain the main methods and attributes of the model delineated before.
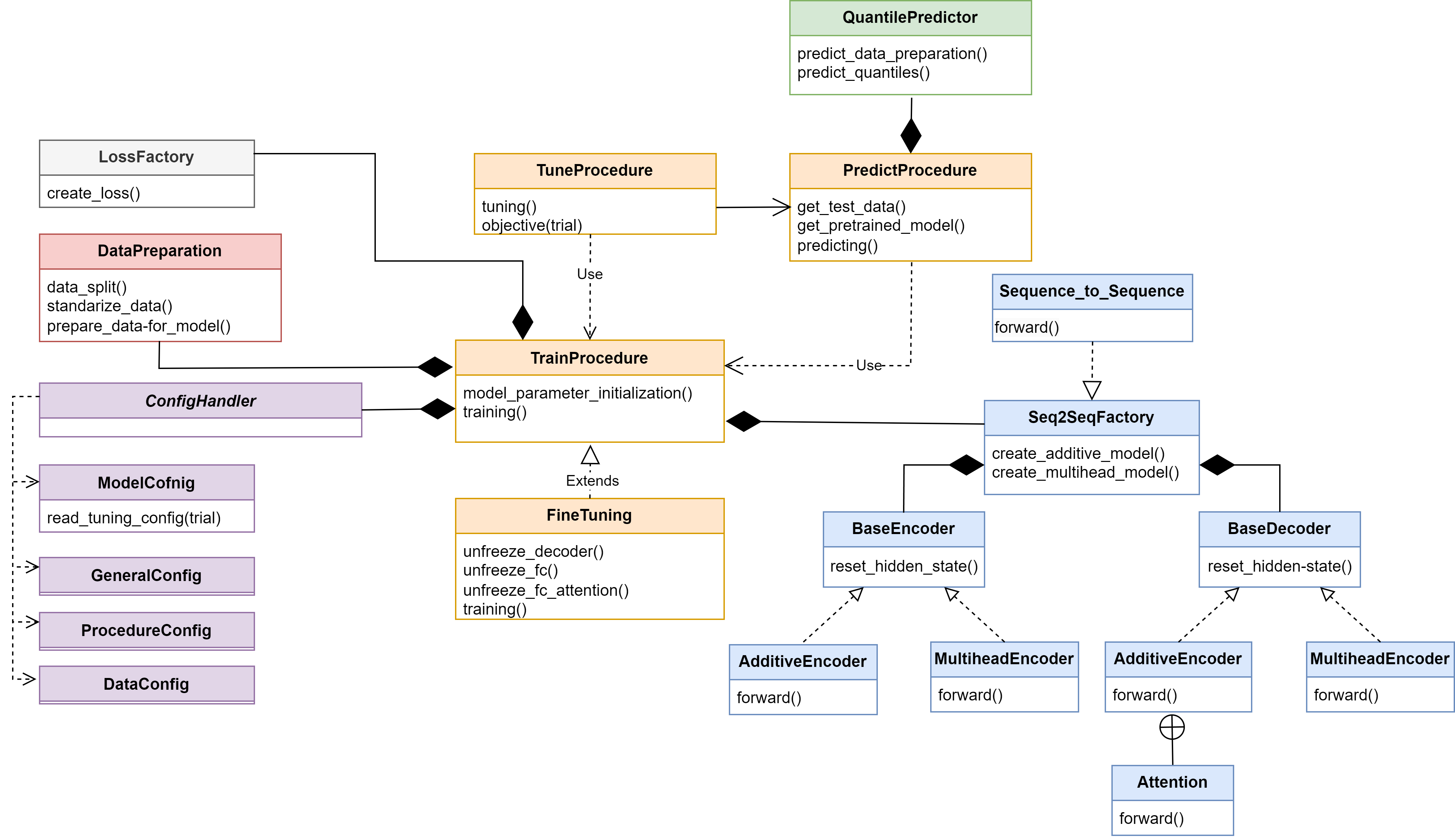
Citation
If you use ARCANA in your research, please cite the following paper, where you can also find its theoretical background and full description:
Rahmanian, F. & Lee R. M., & Linzner, D. & Michel, K. & Merker, L. & Berkes, B. & Nuss, L. & Stein, H.S. (2023). Attention towards chemistry agnostic and explainable battery lifetime prediction. Available at: ChemRxiv (Accessed: [08.12.2023]). DOI:10.26434/chemrxiv-2023-nhdh2-v2
History
0.1.0 (2023-02-01)
First release on GitHub
0.1.1 (2023-08-25)
Updated documentation
Branched off from the original project and added abstractions and modularization
1.0.0 (2023-12-08)
First official release of the ARCANA package
1.0.1 (2024-01-15)
Minor bug fixes and improvements
Project details
Release history Release notifications | RSS feed
Download files
Download the file for your platform. If you're not sure which to choose, learn more about installing packages.
Source Distributions
Built Distribution
Hashes for arcana_batt-1.0.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl
| Algorithm | Hash digest | |
|---|---|---|
| SHA256 | d245183ad533f87b4856e6bc1a009c4be206554574c22f614c2454bac0cd136c |
|
| MD5 | d417fc0e4b1b4e28f2df541e97fd8e99 |
|
| BLAKE2b-256 | eed44cb4c990de2c4bfaa95a30e593b9d25862f3881485ca6d7d99ac9827b3dc |











